Minuscule Bitcoin Amounts, Understanding Microtransactions in Cryptocurrency
In the world of cryptocurrency, the value of Bitcoin can fluctuate significantly, leading to situations where even minuscule amounts such as 0.00001756 BTC can be a topic of interest. This article delves into what such fractional amounts represent, their implications for microtransactions, and how they fit into the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
In the world of cryptocurrency, the value of Bitcoin can fluctuate significantly, leading to situations where even minuscule amounts such as 0.00001756 BTC can be a topic of interest. This article delves into what such fractional amounts represent, their implications for microtransactions, and how they fit into the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
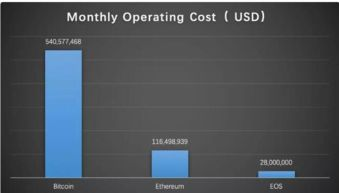
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency, introduced in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a decentralized network called blockchain, allowing users to send and receive value without the need for intermediaries like banks. Bitcoin transactions are recorded on this public ledger, ensuring transparency and security.
Fractional amounts of Bitcoin, such as 0.00001756 BTC, are often referred to as satoshis. One Bitcoin is divisible into 100 million satoshis, making it feasible for microtransactions that traditional currencies might struggle to accommodate due to fees and minimum transaction values.

The Importance of Microtransactions
In recent years, the rise of micropayments has transformed how we view online transactions. Microtransactions refer to very low-value transactions that might be impractical in a traditional finance context. The ability to transact in small Bitcoin amounts opens up various use cases, including:
- Content Monetization: Creators can receive small payments for their work.
- Gaming: Players can make low-cost in-game purchases.
- Charity: Donors can contribute small amounts to multiple causes.
With 0.00001756 BTC equating to a fraction of a cent based on Bitcoin’s market value, these transactions demonstrate how Bitcoin can facilitate everyday dealings without the need for large sum transfers.

Balancing Fees and Value
While the concept of microtransactions is appealing, challenges like transaction fees arise. Bitcoin has seen fluctuations in network fees, sometimes rendering microtransactions non-viable. Factors such as network congestion and individual wallet fees can elevate the cost of sending even minimal amounts, making it essential for developers and platforms to create solutions minimizing these costs.
The Lightning Network, for example, is a second-layer solution designed to enable fast and low-cost transactions, allowing users to transact in fractions of a bitcoin seamlessly. By harnessing systems like these, the potential of using amounts as small as 0.00001756 BTC can become a reality.
In conclusion, 0.00001756 BTC embodies the essence of microtransactions in the cryptocurrency world. While considerable challenges in terms of fees and transaction viability exist, innovative solutions are paving the way for a future where such small amounts facilitate a range of transactions, promoting inclusivity and diversity in the digital economy. The advancements in technology will likely strengthen the relevance of Bitcoin fractions in various sectors worldwide.



