price histroy,Price History: A Comprehensive Guide
Price History: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the price history of a product or asset is crucial for making informed decisions. Whether you are an investor, a consumer, or simply curious about market trends, delving into the past prices can provide valuable insights. In this article, we will explore the various dimensions of price history, including historical data analysis, factors influencing prices, and practical applications.
Historical Data Analysis
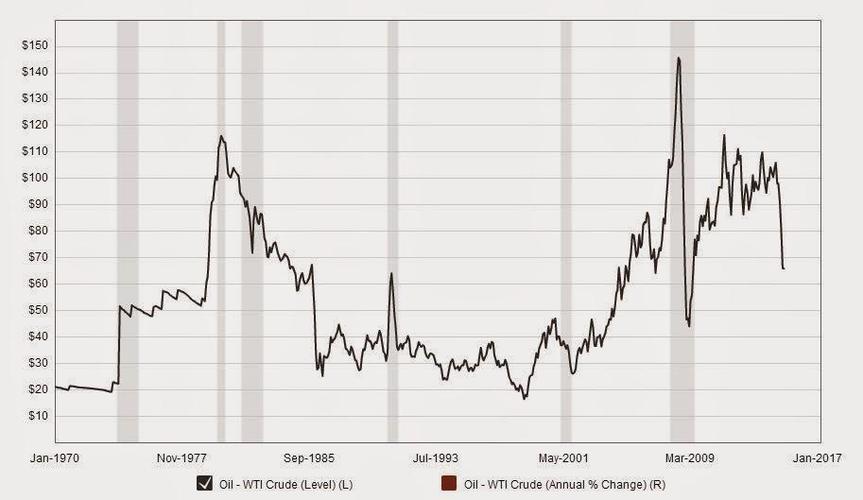
Historical data analysis is the foundation of understanding price history. By examining past prices, you can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may impact future performance. Here are some key aspects to consider:

| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Period | Choose a specific time frame to analyze, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly data. |
| Price Range | Identify the lowest and highest prices within the chosen time frame. |
| Volatility | Measure the degree of price fluctuations over time. |
| Market Trends | Identify upward or downward trends in prices. |
| Seasonality | Observe patterns that occur at specific times of the year. |
By analyzing historical data, you can gain a better understanding of the factors that influence price movements and make more accurate predictions.
Factors Influencing Prices
Several factors can influence the price history of a product or asset. Understanding these factors is essential for interpreting price movements and making informed decisions. Here are some key factors to consider:
-
Economic Indicators: Economic indicators such as GDP, inflation rates, and unemployment rates can impact prices. For example, a strong economy may lead to higher prices, while a weak economy may result in lower prices.
-
Supply and Demand: The balance between supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining prices. If demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise, and vice versa.
-
Market Sentiment: Investor sentiment and market psychology can significantly influence prices. Positive sentiment can drive prices up, while negative sentiment can lead to price declines.
-
Competition: The level of competition in the market can impact prices. Increased competition may lead to lower prices, while limited competition may result in higher prices.
-
Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations or policies can affect prices. For example, new regulations may increase production costs, leading to higher prices.
By considering these factors, you can gain a better understanding of the reasons behind price movements and make more informed decisions.
Practical Applications
Understanding price history has practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples:
-
Investment Decision Making: Investors can use price history to identify undervalued or overvalued assets, making more informed investment decisions.
-
Consumer Purchasing Decisions: Consumers can use price history to identify the best time to purchase a product or asset, taking advantage of price fluctuations.
-
Market Trend Analysis: Businesses can analyze price history to identify market trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
-
Policy Making: Governments and policymakers can use price history to understand market dynamics and make informed decisions regarding regulations and policies.
In conclusion, understanding price history is crucial for making informed decisions in various fields. By analyzing historical data, considering influencing factors, and applying practical applications, you can gain valuable insights into market trends and make more accurate predictions.






